Academic Programs
.Master of Science
.In-Service Master’s Program
Research Highlights
The core and research domains, comprising 1) vision systems and 2) intelligent systems and control techniques, of GIAT are described as follows.
.Vision Systems involving the following related techniques: Digital image processing, Machine vision and image processing algorithms, Automatic optical inspection, medical image processing, 3D image reconstruction, and video servo.
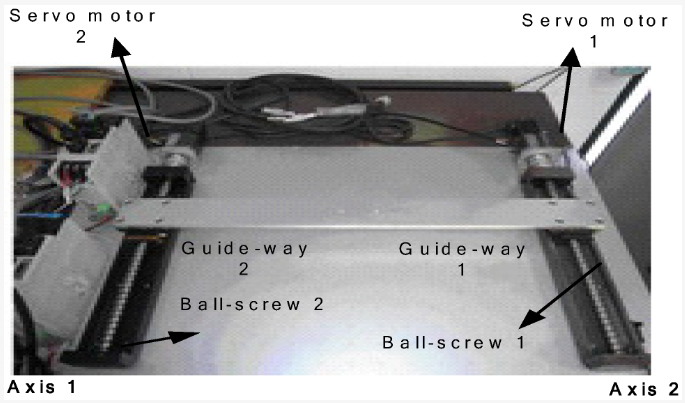
A hardware structure of the gantry robot system, which consists of two rotating servo motors, guideways and ball screws, to be controlled through synchronous control methods—a parallel control method and a parallel master-slave control method
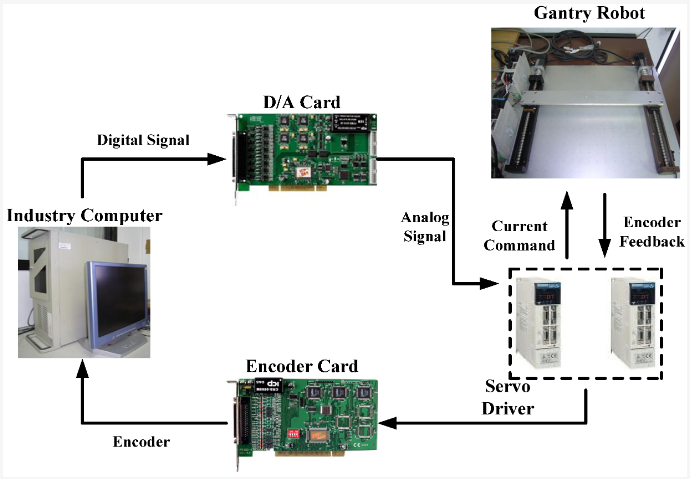
The hardware setup of a PC-based control system to the gantry robot system |
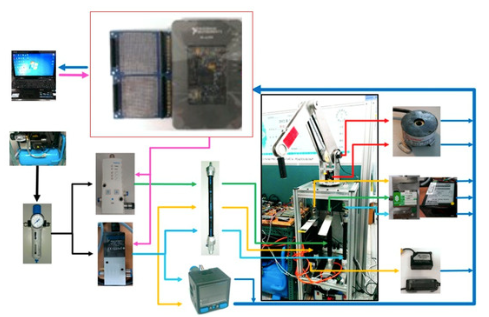
An experimental setup of a robot arm system to be studied, where 1) a dynamic model between the robot arm and the proposed PAM cylinder is defined; 2) the parameters thereof are identified through a Genetic Algorithm; and 3) PID is used along with a high-order sliding-mode feedback controller to perform circular trajectory tracking.
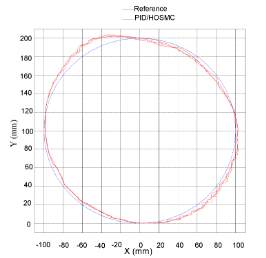
Results of the tracking circular trajectory of a robot arm—the θ2 axis uses PID; the θ1 axis uses HOSMC (high-order sliding-mode control) |
A humanoid robot arm was used to validate the proposed skill learning method. As demonstrated, the robot was able to generate smooth Cartesian and joint trajectories to reach to a cup, grasp it, and pour water. |
.Intelligent systems and control techniques: Artificial Neural Networks, Fuzzy systems, Soft computing, Object-oriented programming techniques, Motion control, applications of Digital Signal Processing, development and applications of embedded systems and real-time multi-task kernels.
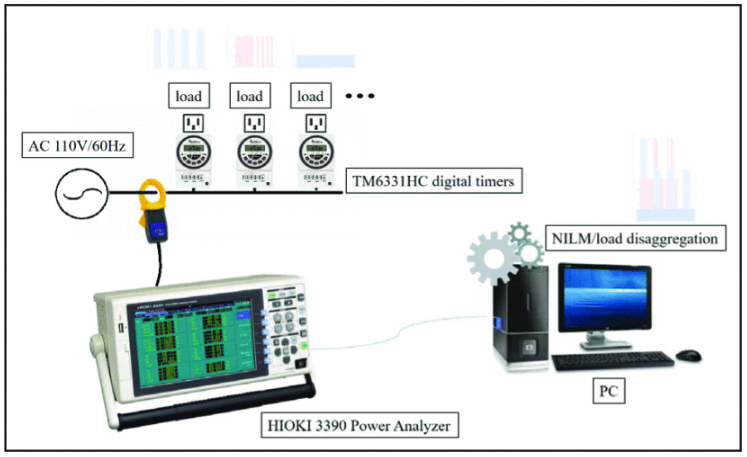
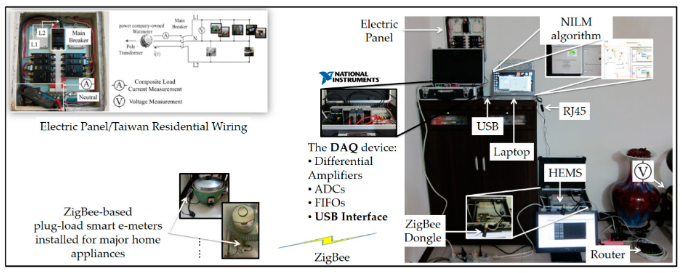
Experiments to the studied NILM under different types of electrical loads
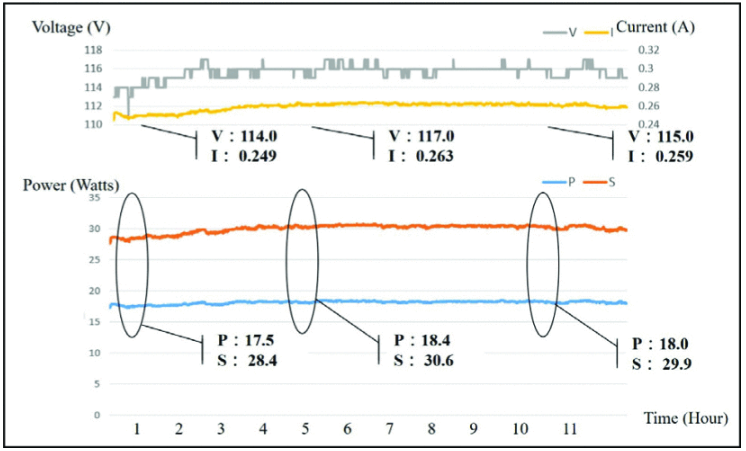
Shown effects of voltage variations to the NILM |
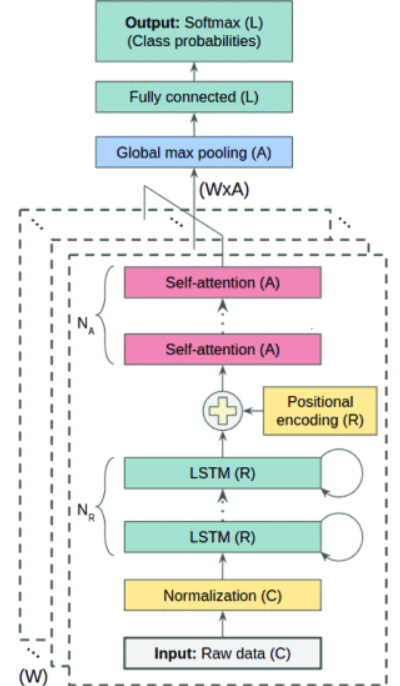
A proposed self-attention network-based HAR neural network architecture
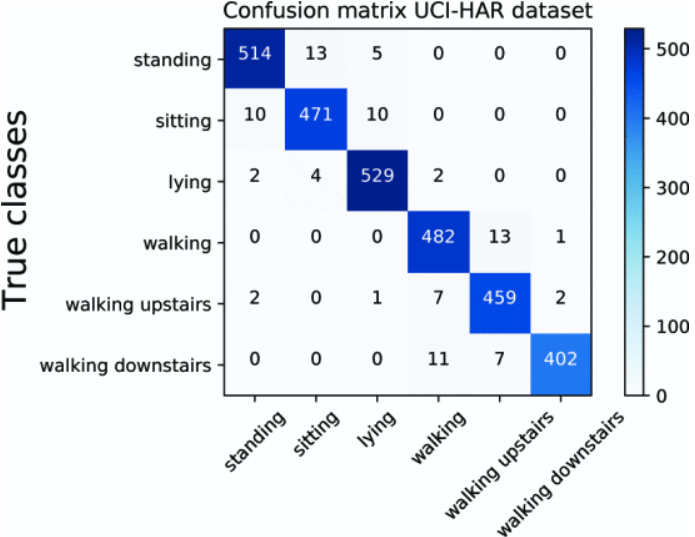
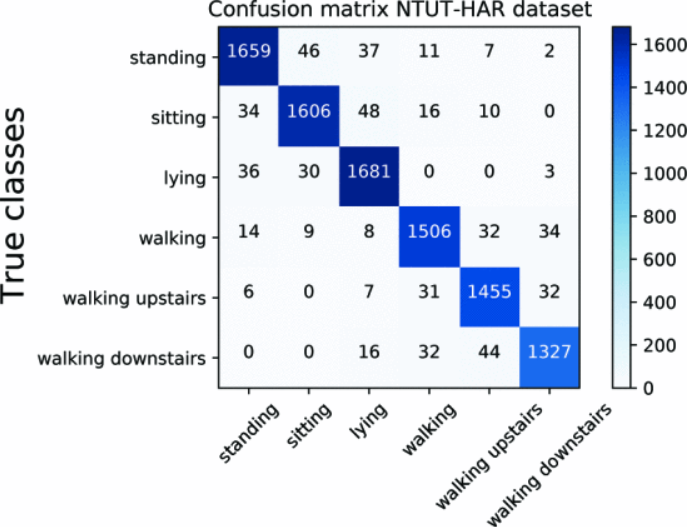
Recognition results by the proposed HAR neural network architecture considering self-attention layers, where it was validated by both the UCI-HAR and NTUT-HAR datasets. |
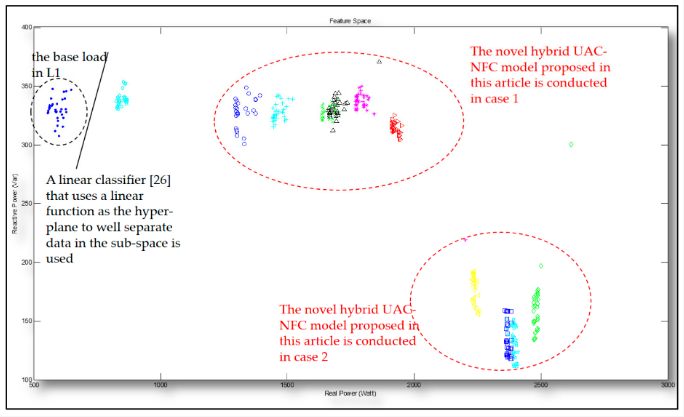
An experimental setup of the IoT-oriented smart HEMS utilizing a proposed novel hybrid UAC-NFC (Unsupervised Automatic Clustering-Integrated Neural-Fuzzy Classification) machine learning model for residential load management in a realistic house environment
Considered feature space being of P (real power) and Q (reactive power) to be modeled and classified for relevant, individual electrical home appliances monitored nonintrusively |
Missions
.To use multi-teaching methods and combine research organizations with the industry for interdisciplinary education, while stressing on worldwide education and providing the opportunity of overseas study for GIAT’s students: the objective is to nurture outstanding automation engineers for the industry.
.To do research on computer vision and intelligent systems for applications in automation industry: the objective is to establish a complete and disciplined research team for industrial research and development.
Learn more about Graduate Institute of Automation Technology-->